boDEREC-CE
In Europe, numerous substances which are known to be inside drinking water are not yet monitored. It is necessary to increase knowledge on those substances because their effects on health and the water ecosystems are still to be fully discovered. Within the boDEREC-CE project, first initiatives have been kicked off to increase the availability of data, knowledge, public awareness, and capacities, in order to be able to propose a transnational strategy, including procedures and tools, for mitigating and managing emerging contaminants (ECs) in the water environment, especially in drinking water. Conducted PPCPs sampling campaigns, hydrological field investigations, and modelling within the pilot actions allowed new and valuable insights into the functioning of water systems as well as the assessment of environmental risks that detected contaminants pose. This is new, precious knowledge on a national, regional, but also at global scale, as the occurrence of PPCPs and their impacts on ecosystems and human health are still insufficiently explored.
boDEREC-CE outputs and results like monitoring and modelling findings, presented at international conferences, workshops and in scientific publications, enabled the dissemination of know-how beyond boundaries of the Central Europe. The consortium countries developed a joint PPCP monitoring methodology, which enabled the comparison of results and transnational cooperation of experts as well as the integration of stakeholders such as practitioners and decision-makers. The large array of stakeholder groups can directly benefit from TRAST-PPCP, a transnational strategy for the mitigation of PPCPs, and from the decision-making support tools wwDEMAST and modePROCON, which can be applied also to regions beyond CE. Transnational cooperation – especially in the new field of mitigation practices - prove to be essential for the project partnership and beyond, in order to contribute to the transnational strategy for ECs control, prevention and mitigation.
Board for detection and assessment
of pharmaceutical drug residues in drinking water
- capacity building for water management in ce
Main aim is:
ESTABLISHment of AN INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT STRATEGY FOR WATERWORKS THAT GUARANTEES INCREASED QUALITY
OF DRINKING WATER
Specific objectives:
STUDIES ON PPCP IN THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT
ESTABLISHment OF DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM FOR WATERWORKS
RECOMENDATION FOR DETAILED PPCP MONITORING IN WATER, INCLUDED MONITORING FROM POTENTIAL PPCP SOURCES, VIA THE WATERCOURSE/THE AQUIFER TO THE WATERWORKS
EVALUATION OF THE TECHNOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF PPCP ATTENUATION IN DRINKING WATER
preparation of A TOOL TO OPTIMIZE TECHNOLOGICAL PROCESES ACCORDING TO RAW WATER QUALITY
PROPOSAL FOR CHANGES TO LEGISLATION ON DRINKING AND WASTEWATER STANDARDS AND TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS
Project in numbers
strategies
tools
pilot actions
Outputs
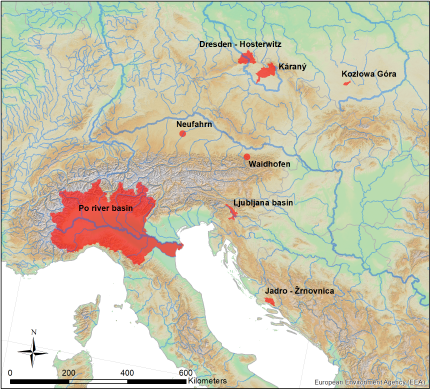
PILOT ACTION AREAS
PILOT ACTION CLUSTER 1 PILOT ACTION CLUSTER 2 PILOT ACTION CLUSTER 3
Surface water: Groundwater: Karst water:
KOZŁOWA GÓRA, PL LJUBLJANA BASIN, SLO JADRO CATCHMENT, CRO
PO RIVER BASIN, IT NEUFAHRN MUNCHEN, GER WAIDHOFEN/YBBS, AUS
DRESDEN - HOSTERWITZ, GER KARANY-JIZERA, CZE
Thematic work package 1
Results
STATE-OF-THE-ART
The main goal was to define state-of-the-art of emerging contaminants appearing in the water environment. Partners were working on this starting from the very beginning of the project. Now we present you two main outputs summarizing findings of nearly 2 years intensive cooperation.
Find more...

Thematic work package 2
Results
MONITORING
The main aim was a definition of the concept of long-term detailed monitoring of time-space changes of PPCP concentrations from the source of water used for the production of potable water up to the process of its technological modification to the final form.
Learn more...

Thematic work package 3
Results
MODELING
The activities included a transnational review of existing country-specific frameworks for model applications in all parts of water management systems. Modelling studies of the water system were conducted within pilot action. One of the main aims of the WPT3 was to develop a model-based decision-making process for emerging contaminants (modePROCON).
Learn more...

Thematic work package 4
Results
NEW APPROACHES
The realisation of the WPT4 aimed at capacity building of the findings gained within the boDEREC-CE project. One of the main aspects was delivering the tools and strategy dedicated to the main stakeholders - the waterworks and water-oriented actors.
Learn more...

NEWS
Taking cooperation forward

project duration
01.04.2019
31.03.2022